With the rapid growth of solar energy and distributed power systems, solar battery backup systems for homes have become a necessity rather than a luxury. This article explains the entire lifecycle of a solar battery system — from planning to recycling — and provides a practical guide on how to choose the best-performing, most reliable, and reasonably priced battery in today’s booming Chinese market, where new manufacturers are emerging like bamboo shoots after spring rain.

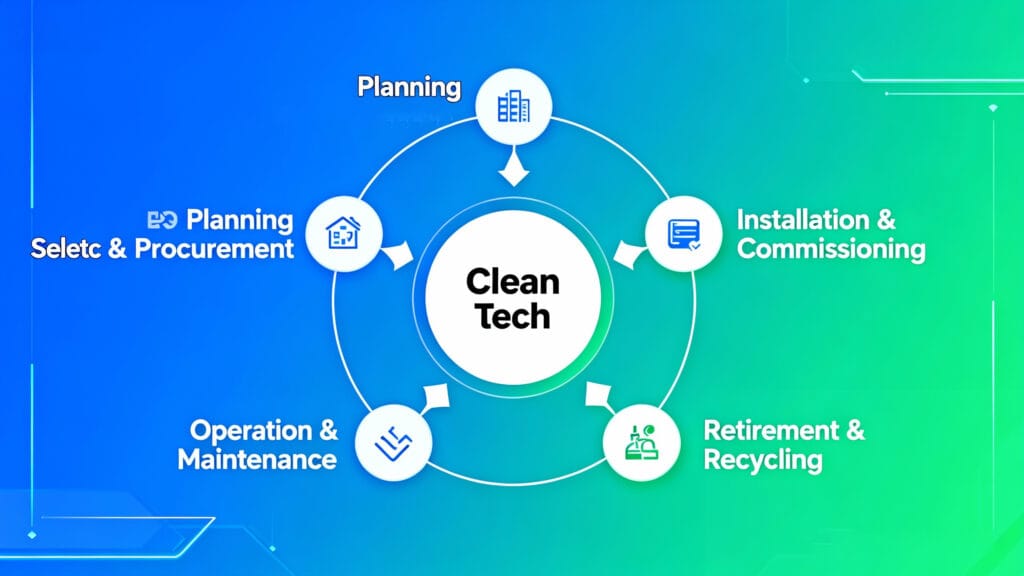
I. Overview of the Solar Battery Backup Lifecycle
- Planning Stage: Understanding Your Needs
- Purpose: Determine whether you need the system for nighttime self-consumption, peak-shaving, emergency backup, or energy trading. Your use case will define the system size and power rating.
- Load Assessment: List essential appliances (fridge, router, lights, water heater, air conditioner, etc.), calculate both continuous and peak loads, and identify required capacity and output power.
- Site Evaluation: Consider roof size, orientation, and sunlight hours to estimate your photovoltaic (PV) array size and battery charge/discharge strategy.
- Selection & Procurement Stage
- Choose the right battery chemistry (LiFePO₄, NMC, lead-acid, etc.). LiFePO₄ batteries are widely favored for their superior safety and long cycle life.
- Evaluate capacity (kWh), nominal voltage, discharge rate (C-rate), and maximum continuous and peak discharge power.
- Examine the BMS (Battery Management System), modular design, cooling methods, and scalability (parallel/series connection).
- Check certifications (CE, IEC, UN38.3, ISO9001, etc.) and warranty coverage (years of coverage, cycle life guarantee, and after-sales service).
- Installation & Commissioning Stage
- Hire qualified installers to ensure proper grid/off-grid switching, grounding, ventilation, and fire safety compliance.
- Fine-tune the system: synchronize inverter and battery settings (charging priorities, SOC limits, and backup modes).
- Validate capacity during the first month: monitor charging efficiency, usable capacity, and temperature performance.
- Operation & Maintenance Stage
- Use apps or online dashboards to monitor SOC (state of charge), cycle count, temperature, and charging behavior.
- Maintenance is minimal for LiFePO₄ systems, but ensure good ventilation, stable temperature, and check wiring connections regularly.
- Optimize settings: avoid full 100% charge or 0% discharge cycles — keeping between 10–95% SOC can extend lifespan.
- Retirement & Recycling Stage
- When battery capacity drops below ~70% or reaches end-of-life, consider replacement or repurposing for lower-demand applications.
- Follow certified recycling channels to safely handle lithium batteries and avoid environmental harm.
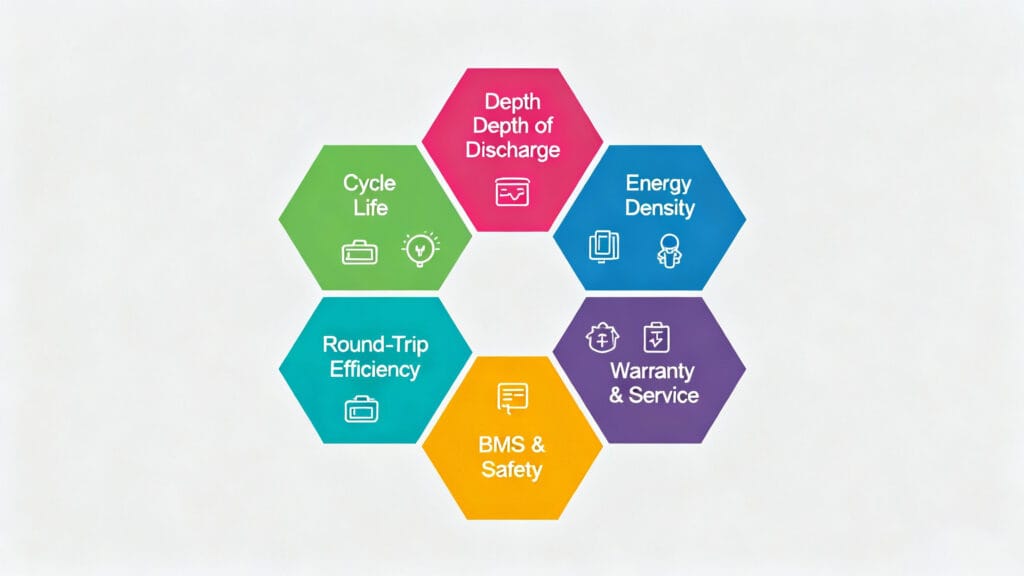
II. Six Key Performance Indicators You Must Know Before Buying
- Cycle Life – The number of charge/discharge cycles before capacity drops to a specific level (e.g., 80%).
- Depth of Discharge (DoD) – The percentage of energy used per cycle. Higher DoD means shorter cycle life, so it must be balanced.
- Energy Density – Affects space and weight. Home users typically prioritize safety and longevity over compactness.
- Round-Trip Efficiency – Measures total energy loss between charging and discharging; higher efficiency saves energy.
- BMS & Safety Design – Determines safety, real-time monitoring, and thermal management. A smart BMS ensures long-term reliability.
- Warranty & Service – Warranty duration, coverage conditions, and after-sales responsiveness define overall peace of mind.
III. In the Face of So Many Chinese Manufacturers, How Do You Identify Reliable Ones?
China’s energy storage industry is booming — countless new brands and factories appear almost overnight. Here’s how to filter quality from chaos:
- Request Real Evidence, Not Just Brochures
- Ask for third-party testing reports, safety certifications, and performance data for specific models.
- If possible, visit the factory or request a live video inspection to verify production capacity and testing facilities.
- Check Cell and BMS Sources
- Many small factories use cells from large manufacturers (CATL, BYD, Gotion, etc.) — this is acceptable if verified.
- Ensure the BMS is from a reputable supplier and supports remote updates and real-time diagnostics.
- Evaluate Quality Control Systems
- Confirm the factory conducts incoming inspection, aging tests, and final capacity verification.
- Lack of these tests often means inconsistent performance and safety risks.
- Examine Warranty and Service Policies
- Review what’s covered under warranty (battery pack, BMS, inverter compatibility), how long, and who bears shipping costs.
- A low price often means weak after-sales service — prioritize brands with established service centers or local support.
- Don’t Chase the Lowest Price
- Extremely low prices usually mean compromises in materials, testing, or support.
- Compare cost per usable kWh over lifetime, not just upfront price — that’s the true measure of value.

IV. Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting Your Solar Battery System
- Define Your Goal & Budget – Do you need emergency backup (3–6 hours) or full-day self-consumption?
- Shortlist 3–5 Brands – Based on certifications, reviews, and test data.
- Request Detailed Technical Documents – Cycle life reports, efficiency curves, BMS specs, and scalability options.
- Ask for Demonstrations or Samples – For large purchases or long-term projects.
- Compare Lifetime Cost, Not Just Purchase Cost – Include replacement, maintenance, and efficiency losses.
- Sign Detailed Warranty Agreements – Ensure clarity on capacity retention, service response, and replacement policy.
V. Common Home Configurations & Cost Insights
- Small Homes (2–4 kWh daily backup): 3–5 kWh LiFePO₄ battery, suitable for lighting, routers, and small appliances.
- Medium Homes (6–12 kWh daily): 5–10 kWh system with 2–4 kW continuous output and high peak load capacity.
- Cost Comparison: Consider inverter, wiring, installation, and service — not just the battery.
The best metric is cost per usable kWh over system lifetime, typically over a 10-year period.
VI. Practical Tips to Extend Battery Lifespan
- Avoid keeping batteries at 100% SOC for long periods; cap charging at 95%.
- Prevent operation under extreme temperatures (below 0°C or above 45°C).
- Regularly check BMS logs for voltage imbalance or internal resistance growth.
- When capacity drops to 70–80%, repurpose for less demanding backup use to maximize ROI.
VII. Conclusion: Balancing Performance, Safety, and Cost in a Crowded Market
A solar battery backup system isn’t a disposable appliance — it’s a long-term investment in energy independence, safety, and sustainability.
In a market flooded with new Chinese manufacturers, the key is not fear, but discernment:
- Define your energy goals and budget clearly;
- Focus on battery chemistry, cycle life, BMS safety, and after-sales support instead of just price;
- Evaluate lifetime cost per kWh and warranty reliability before purchase;
- Choose brands with verified test reports, certifications, and real customer service networks — even if they cost a bit more upfront.
In the long run, a well-chosen solar battery is not only a reliable power source but also a wise financial and environmental decision.